Electrical Power System: An In-Depth Explanation
Electricity is an essential part of our daily lives, and it is supplied to us through a complex network of power systems. Electrical power systems consist of various components that work together to generate, transmit, distribute, and control electricity. In this article, we will take an in-depth look at the electrical power system, its components, and how they work together to provide us with reliable and uninterrupted electricity.
Introduction to Electrical Power System
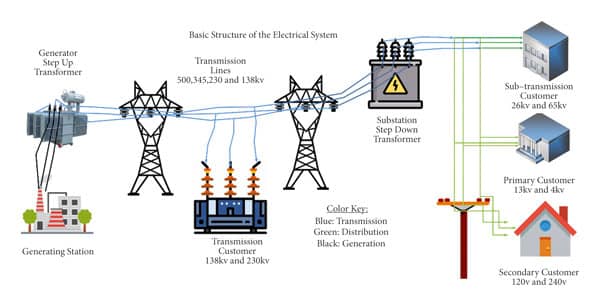
The electrical power system is a network of components that generate, transmit, distribute, and control electrical power. The power system consists of four main components: generation, transmission, distribution, and control. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring that the electricity is supplied efficiently and reliably to the end-users.
Generation
The generation component of the electrical power system is responsible for producing electrical energy from various sources. The primary sources of electrical energy are fossil fuels, nuclear energy, and renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, and hydro. The generators convert the mechanical energy produced by these sources into electrical energy.
Transmission
The transmission component of the electrical power system is responsible for transmitting the electrical energy from the generation sources to the distribution system. The transmission lines carry high voltage electricity over long distances to minimize power losses.
Distribution
The distribution component of the electrical power system is responsible for distributing the electrical energy from the transmission system to the end-users. The distribution system consists of transformers, switchgear, and distribution lines that supply electricity to residential, commercial, and industrial consumers.
Control
The control component of the electrical power system is responsible for monitoring and controlling the generation, transmission, and distribution components to ensure that the system operates efficiently and reliably. The control system uses advanced technologies such as Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) and Energy Management Systems (EMS) to monitor and control the power system.
Components of Electrical Power System
The electrical power system consists of several components that work together to generate, transmit, distribute, and control electrical power. Let’s take a closer look at the components of the electrical power system.
Power Generation
The power generation component consists of generators that convert the mechanical energy produced by various sources into electrical energy. The generators are driven by steam turbines, gas turbines, or hydro turbines, depending on the source of energy.
Transformers
Transformers are essential components of the electrical power system that are used to step-up or step-down the voltage of the electricity. The step-up transformers increase the voltage of the electricity for transmission, while the step-down transformers decrease the voltage for distribution to end-users.
Transmission Lines
Transmission lines are used to transmit high voltage electricity over long distances with minimal power losses. The transmission lines are made up of conductors, insulators, and supporting structures.
Substations
Substations are electrical facilities that are used to switch, control, and protect the electrical power system. They are also used to step-up or step-down the voltage of the electricity.
Distribution Lines
Distribution lines are used to distribute electricity to end-users such as residential, commercial, and industrial consumers. The distribution lines are typically mounted on poles or underground.
Capacitors and Reactors
Capacitors and reactors are used to regulate the voltage and current of the electricity. Capacitors are used to improve the power factor of the electrical system, while reactors are used to limit the current flow.
Switchgear
Switchgear is used to control and protect the electrical power system from faults and overloads. It includes circuit breakers, disconnect switches, and fuses.
How Electrical Power System Works
The electrical power system works in a complex and integrated manner to ensure that the electricity is supplied efficiently and reliably to end-users. Let’s take a closer look at how the electrical power system works.
Generation
The first step in the process of generating electricity is to produce mechanical energy from various sources such as fossil fuels, nuclear energy, wind, solar, or hydro. The generators then convert this mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Transmission
The high voltage electrical energy produced by the generators is transmitted over long distances through transmission lines to minimize power losses. The transmission lines are designed to carry the electricity over large distances without significant losses.
Substations
The electricity is then received at a substation, where it is stepped down to a lower voltage for distribution to end-users. The substation also controls and protects the electrical power system from faults and overloads.
Distribution
The electricity is then distributed to end-users through distribution lines. The distribution lines are typically mounted on poles or underground, depending on the location and environment.
End-User Consumption
The end-users receive the electricity and consume it in various ways, such as lighting, heating, cooling, and powering electronic devices.
Control and Monitoring
The electrical power system is continuously monitored and controlled using advanced technologies such as Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) and Energy Management Systems (EMS). These systems ensure that the power system operates efficiently and reliably.
Challenges in Electrical Power System
The electrical power system faces several challenges, such as aging infrastructure, increasing demand for electricity, renewable energy integration, and cybersecurity threats.
Aging Infrastructure
The electrical power system’s infrastructure, such as transformers, switchgear, and transmission lines, is aging and needs significant investments to maintain and upgrade.
Increasing Demand for Electricity
The demand for electricity is increasing, driven by population growth, urbanization, and industrialization. The electrical power system needs to adapt to meet the increasing demand for electricity.
Renewable Energy Integration
The integration of renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, into the electrical power system presents several challenges, such as intermittent generation and voltage stability.
Cybersecurity Threats
The electrical power system is vulnerable to cybersecurity threats, such as cyberattacks, which can cause significant disruptions to the power system’s operations.
Conclusion
The electrical power system is a complex network of components that work together to generate, transmit, distribute, and control electricity. It is a critical infrastructure that plays a crucial role in our daily lives. The electrical power system faces several challenges, such as aging infrastructure, increasing demand for electricity, renewable energy integration, and cybersecurity threats. To ensure that the electrical power system remains reliable and efficient, it requires significant investments in infrastructure, technology, and cybersecurity.
FAQs
- What is an electrical power system?
- A. An electrical power system is a network of components that generate, transmit, distribute, and control electrical power.
- What are the components of the electrical power system?
- A. The components of the electrical power system are generation, transmission, distribution, and control.
- How does the electrical power system work?
- A. The electrical power system works by generating electrical energy from various sources, transmitting the electricity over long distances through transmission lines, stepping down the voltage at substations, distributing the electricity to end-users through distribution lines, and controlling and monitoring the power system using advanced technologies.
- What are the challenges in the electrical power system?
- A. The challenges in the electrical power system are aging infrastructure, increasing demand for electricity, renewable energy integration, and cybersecurity threats.
- What is the role of SCADA and EMS in the electrical power system?
- A. SCADA and EMS are advanced technologies used to monitor and control the electrical power system
- What is electrical power?
- A. Electrical power is the rate at which electrical energy is transferred or converted to another form of energy.
- What is the difference between AC and DC power?
- A. AC (alternating current) power changes direction periodically, while DC (direct current) power flows in only one direction.
- How is electricity measured?
- A. Electricity is measured in units of power called watts, which is equal to voltage multiplied by current.
- What is the purpose of a transformer in the electrical power system?
- A. A transformer is used to transfer electrical energy from one circuit to another by means of electromagnetic induction.
- What is the role of a generator in the electrical power system?
- A. A generator is used to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- What is a synchronous generator?
- A. A synchronous generator is a type of generator that generates AC power at a specific frequency that is synchronized with the power grid.
- What is a frequency converter?
- A. A frequency converter is used to convert the frequency of AC power from one value to another.
- How does the electrical power system ensure power quality?
- A. The electrical power system uses various methods such as voltage regulation, power factor correction, and harmonic filtering to ensure power quality.
- What is load shedding?
- A. Load shedding is a method used by the electrical power system to reduce the demand for power by selectively disconnecting certain loads from the grid.
- What is a black start generator?
- A. A black start generator is a generator that can be started without an external power source, and is used to restore power to the grid after a blackout or other emergency situation.
- What is a circuit breaker?
- A. A circuit breaker is an electrical switch that automatically cuts off power to a circuit in the event of an overload or short circuit.
- How does the electrical power system manage power surges and outages?
- A. The electrical power system uses surge protectors, voltage regulators, and backup power systems to manage power surges and outages.
- What is a brownout?
- A. A brownout is a temporary reduction in voltage in an electrical power system, often caused by high demand or a fault in the system.
- How does the electrical power system manage voltage fluctuations?
- A. The electrical power system uses voltage regulators and capacitors to manage voltage fluctuations.
- What is a smart grid?
- A. A smart grid is an advanced electrical power system that uses digital communication and control technologies to improve efficiency and reliability.
- What is a microgrid?
- A. A microgrid is a localized electrical power system that can operate independently of the main grid, often using renewable energy sources.
- What is a distributed generation system?
- A. A distributed generation system is a small-scale power generation system that is located close to the point of use, such as a rooftop solar panel.
- How does the electrical power system ensure grid stability?
- A. The electrical power system uses various methods such as frequency regulation, voltage regulation, and reactive power control to ensure grid stability.
- What is a power flow analysis?
- A. A power flow analysis is a method used to analyze the flow of power through an electrical power system.
- What is a fault analysis?
- A. A fault analysis is a method used to analyze faults in an electrical power system, such as short circuits or ground faults.
- What is a relay?
- A. A relay is an electrical switch that is operated by an electromagnet, and is used to control the flow of current in a circuit.
- How does the electrical power system manage reactive power?
- A. The electrical power system uses devices such as capacitors and synchronous condensers to manage reactive power.
- What is a capacitor bank?
- . A capacitor bank is a collection of capacitors that are connected together to provide a specific amount of reactive power to the electrical power system.
- What is a switchgear?
- . Switchgear is a combination of electrical devices such as circuit breakers, fuses, and switches that are used to protect, control, and isolate electrical equipment.
- What is a substation?
- . A substation is a part of the electrical power system that is used to transform voltage levels and distribute power to different parts of the grid.
- What is a power transformer?
- . A power transformer is a device used to transfer electrical energy from one circuit to another through electromagnetic induction, while changing the voltage and current levels.
- What is a step-up transformer?
- . A step-up transformer is a transformer that increases the voltage of the electrical energy being transferred.
- What is a step-down transformer?
- A. A step-down transformer is a transformer that decreases the voltage of the electrical energy being transferred.
- What is an autotransformer?
- A. An autotransformer is a transformer that uses a single winding to transfer electrical energy between circuits, while adjusting the voltage level.
- What is a distribution transformer?
- A. A distribution transformer is a transformer that is used to lower the voltage of the electrical energy being distributed to households and businesses.
- What is a transmission line?
- A. A transmission line is a high-voltage power line that is used to transport electrical energy over long distances.
- What is a circuit protection device?
- A. A circuit protection device is a device that is used to protect electrical equipment from damage due to overcurrent or short circuits.
- What is a grounding system?
- A. A grounding system is a system of conductors that is used to provide a low-impedance path to the earth for fault currents.
- What is a lightning arrester?
- A. A lightning arrester is a device that is used to protect electrical equipment from damage due to lightning strikes.
- What is a power factor?
- A. Power factor is a measure of the efficiency of the electrical power system, and is the ratio of real power to apparent power.
- What is a reactive power?
- A. Reactive power is the portion of electrical power that is consumed by devices such as motors and transformers, without doing useful work.
- What is a harmonic distortion?
- A. Harmonic distortion is a type of electrical interference that can occur in the electrical power system, caused by non-linear loads.
- What is a load tap changer?
- A. A load tap changer is a device that is used to change the voltage ratio of a transformer while it is in operation.
- What is a power factor correction capacitor?
- A. A power factor correction capacitor is a capacitor that is used to correct the power factor of the electrical power system.
- What is a surge protector?
- A. A surge protector is a device that is used to protect electrical equipment from damage due to voltage surges.
- What is a voltage regulator?
- A. A voltage regulator is a device that is used to regulate the voltage of the electrical power system.
- What is a power distribution system?
- A. A power distribution system is a system that is used to distribute electrical power from the power source to the end users.
- What is a feeder?
- A. A feeder is a part of the electrical power system that is used to distribute power to a specific area or group of customers.
- What is a busbar?
- A. A busbar is a conductor that is used to distribute electrical power to different parts of the electrical power system.
- What is a load center?
- A. A load center is a part of the electrical power system that is used to distribute power to individual customers or groups of customers.
- What is an electrical grid?
- A. An electrical grid is a network of interconnected power generation, transmission, and distribution systems that are used to supply electricity to consumers.
- What is a black start?
- A. A black start is the process of restoring power to an electrical power system after a complete shutdown or blackout.
- What is an outage?
- A. An outage is a disruption in the supply of electricity to a particular area or customer.
- What is an interruptible load?
- A. An interruptible load is a type of load that can be turned off or reduced in response to a request from the electrical power system operator.
- What is a load shedding?
- A. Load shedding is the deliberate reduction or interruption of power supply to certain areas or customers in order to prevent a total system collapse during periods of high demand.