All About SPC: A Comprehensive Guide
As businesses strive to improve their production processes, quality control becomes a crucial aspect to ensure customer satisfaction. Statistical Process Control (SPC) is a tool used to monitor and control a process by analyzing its statistical data. In this article, we will provide you with a comprehensive guide on SPC, including its definition, benefits, application, and implementation.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is SPC?
- Benefits of SPC
- Application of SPC
- Implementation of SPC
- Step 1: Define the process
- Step 2: Collect data
- Step 3: Analyze the data
- Step 4: Implement corrective actions
- Step 5: Monitor and control the process
- Common Tools used in SPC
- Control Charts
- Pareto Charts
- Histograms
- Scatter Diagrams
- SPC and Six Sigma
- SPC in Manufacturing and Service Industries
- Challenges in Implementing SPC
- Training Requirements for SPC
- Conclusion
- FAQs
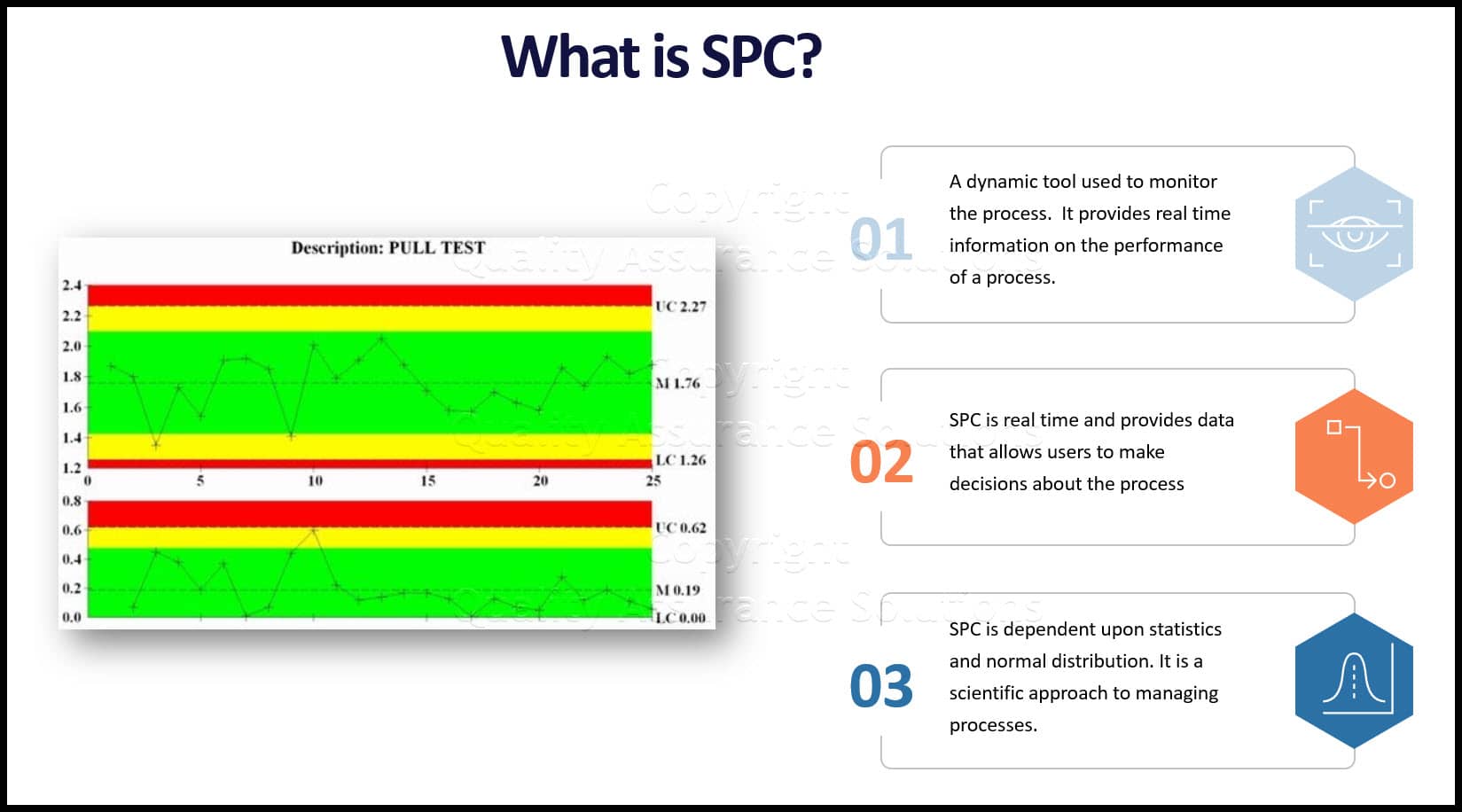
What is SPC?
Statistical Process Control (SPC) is a statistical method used to monitor and control a process by analyzing its statistical data. It is an essential tool for quality control in manufacturing and service industries, where the process output is variable, and the quality of the output is critical to meet customer expectations.
In SPC, data is collected over time to understand the process’s variation and identify the sources of variation. SPC involves statistical analysis of data to identify patterns, trends, and other changes in the process. The data is then used to make informed decisions to improve the process.
Benefits of SPC
Implementing SPC has several benefits, including:
- Improved product quality: SPC helps to identify and eliminate the sources of variation in the process, resulting in consistent product quality.
- Cost reduction: By reducing variation and improving quality, SPC helps to reduce costs associated with rework, scrap, and customer complaints.
- Improved productivity: SPC helps to identify process improvements, resulting in increased productivity and efficiency.
- Improved customer satisfaction: Consistent product quality leads to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Early detection of problems: SPC helps to detect problems early, before they become major issues, reducing the need for costly and time-consuming corrective actions.
Application of SPC
SPC can be applied to any process that produces a variable output, including:
- Manufacturing processes
- Service processes
- Administrative processes
- Healthcare processes
- Financial processes
Implementation of SPC
Implementing SPC involves the following steps:
Step 1: Define the process
The first step in implementing SPC is to define the process that needs to be monitored and controlled. This involves identifying the process inputs, outputs, and variables that will be measured.
Step 2: Collect data
Data collection is a crucial step in SPC. The data collected should be representative of the process and should include all variables that may affect the process output. The data should be collected over time to identify patterns and trends in the process.
Step 3: Analyze the data
The data collected is analyzed to identify patterns, trends, and other changes in the process. Control charts, histograms, Pareto charts, and scatter diagrams are commonly used in SPC to analyze data.
Step 4: Implement corrective actions
Based on the analysis of data, corrective actions are implemented to address any issues identified in the process.
Step 5: Monitor and control the process
Once corrective actions have been implemented, the process is monitored to ensure that the changes have resulted in improved process performance. Data is continually collected and analyzed to ensure that the process remains under control and to identify any new issues that may arise.
Common Tools used in SPC
Several tools are used in SPC to analyze data and identify patterns and trends in the process. Some of the commonly used tools are:
Control Charts
Control charts are graphical tools used to monitor process performance over time. They show the process’s central tendency and its variability, allowing process operators to identify when the process is out of control.
Pareto Charts
Pareto charts are used to identify the most significant sources of variation in the process. They help process operators prioritize improvement efforts by identifying the critical few issues that are responsible for the majority of the process’s problems.
Histograms
Histograms are graphical representations of data that show the frequency distribution of a variable. They help process operators understand the process’s variability and identify potential sources of variation.
Scatter Diagrams
Scatter diagrams are used to identify the relationship between two variables. They help process operators identify patterns and trends in the process and identify potential sources of variation.
SPC and Six Sigma
SPC is a critical tool in the Six Sigma methodology, which is a data-driven approach to quality improvement. Six Sigma focuses on reducing process variation and defects to achieve consistent and predictable process performance.
SPC is used in the Measure and Control phases of the Six Sigma DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) process. In the Measure phase, SPC is used to collect and analyze data to understand the process’s baseline performance. In the Control phase, SPC is used to monitor and control the process to ensure that the improvements made are sustained.
SPC in Manufacturing and Service Industries
SPC is widely used in manufacturing industries to monitor and control production processes. It is also used in service industries to monitor and control service delivery processes.
In manufacturing, SPC is used to monitor and control critical process parameters to ensure that the product meets the desired quality standards. In service industries, SPC is used to monitor and control the service delivery process to ensure that the customer receives a consistent and high-quality service.
Challenges in Implementing SPC
Implementing SPC can be challenging due to several factors, including:
- Lack of understanding of statistical methods
- Resistance to change
- Lack of commitment from management
- Insufficient data collection and analysis
- Inadequate training of employees
To overcome these challenges, it is essential to provide adequate training to employees and management, establish a culture of continuous improvement, and allocate sufficient resources to the implementation of SPC.
Training Requirements for SPC
Training is essential to ensure that employees and management understand SPC’s principles and can effectively implement it in the organization. Training should cover the following topics:
- Basic statistical methods
- SPC principles and techniques
- Data collection and analysis
- Control chart interpretation
- Corrective action implementation
Conclusion
SPC is a powerful tool for quality control that can help organizations improve their production processes and meet customer expectations. By collecting and analyzing statistical data, SPC can identify sources of variation in the process and provide insights into how to improve it. Implementing SPC requires commitment from management and employees and adequate training to ensure its successful implementation.
FAQs
- Q. What is the difference between SPC and SQC?
- A. SPC is a type of Statistical Quality Control (SQC) that focuses on monitoring and controlling a process’s statistical data to ensure consistent quality output.
- Q. What is the role of SPC in Six Sigma?
- A. SPC is a critical tool in the Six Sigma methodology, where it is used to monitor and control process performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Q. What are the benefits of using SPC in manufacturing?
- A. Using SPC in manufacturing
- Q. Can SPC be used in service industries?
- A. Yes, SPC can be used in service industries to monitor and control service delivery processes and ensure consistent quality service.
- Q. What are some common tools used in SPC?
- A. Some common tools used in SPC include control charts, Pareto charts, histograms, and scatter diagrams.
- Q. What are the challenges in implementing SPC?
- A. Some challenges in implementing SPC include lack of understanding of statistical methods, resistance to change, lack of commitment from management, insufficient data collection and analysis, and inadequate training of employees.
- Q. What training is required for implementing SPC?
- A. Training on basic statistical methods, SPC principles and techniques, data collection and analysis, control chart interpretation, and corrective action implementation is essential for effective implementation of SPC.