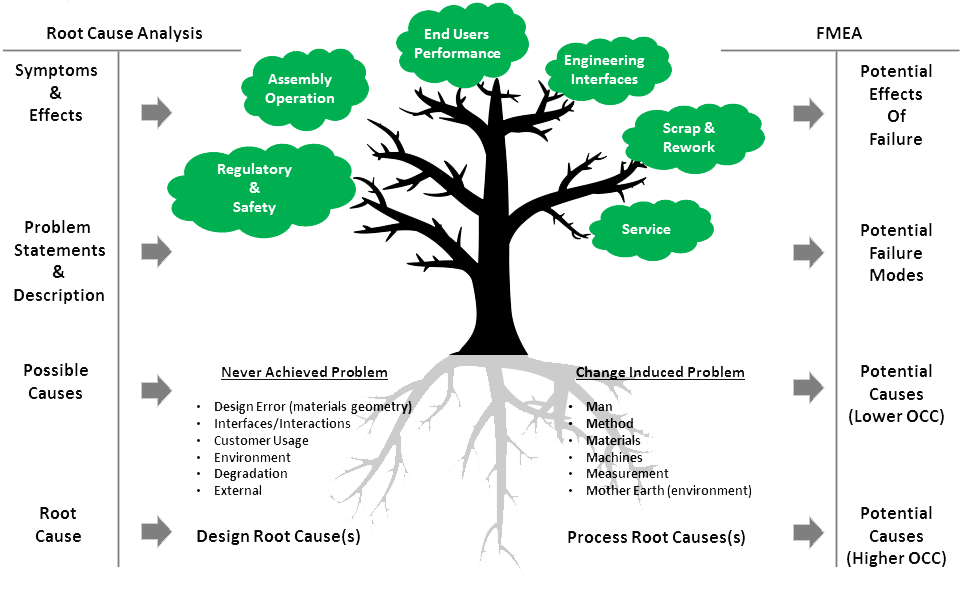
Root Cause Analysis Process: Understanding the Basics
Root cause analysis (RCA) is a method used to identify the underlying cause of a problem or an event. The process helps in identifying the root cause and then taking corrective actions to prevent the problem from recurring. In this article, we will cover the basics of root cause analysis, including what it is, its benefits, and the steps involved in the RCA process.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Root Cause Analysis
- Benefits of Root Cause Analysis
- Steps Involved in Root Cause Analysis
- Step 1: Define the Problem
- Step 2: Collect Data
- Step 3: Identify Possible Causes
- Step 4: Analyze the Data
- Step 5: Identify the Root Cause
- Step 6: Implement Corrective Actions
- Step 7: Monitor the Results
- Tools and Techniques Used in Root Cause Analysis
- Common Mistakes to Avoid in RCA
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
Root cause analysis is a crucial process in identifying the underlying causes of problems, events, or incidents. The RCA process helps organizations to understand the root cause of a problem and develop effective solutions to prevent the problem from recurring. Root cause analysis is widely used in various industries, including healthcare, manufacturing, and aviation, to name a few.
Definition of Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis is a systematic process used to identify the underlying cause or causes of an event, problem, or incident. The RCA process involves identifying the problem, collecting data, identifying possible causes, analyzing the data, identifying the root cause, implementing corrective actions, and monitoring the results. The goal of RCA is to prevent the problem from recurring by addressing the root cause.
Benefits of Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis provides many benefits, including:
- Helps identify the root cause of a problem, which helps prevent the problem from recurring.
- Improves the efficiency and effectiveness of processes by identifying areas for improvement.
- Reduces the risk of future incidents or accidents.
- Promotes a culture of continuous improvement within the organization.
- Increases customer satisfaction by improving the quality of products or services.
Steps Involved in Root Cause Analysis
The RCA process typically involves the following seven steps:
Step 1: Define the Problem
The first step in RCA is to define the problem. This involves clearly identifying the problem, its scope, and its impact on the organization.
Step 2: Collect Data
The second step is to collect data. This involves gathering information about the problem, including when it occurred, how it occurred, and who was involved.
Step 3: Identify Possible Causes
The third step is to identify possible causes. This involves brainstorming all possible causes of the problem and then narrowing down the list to the most likely causes.
Step 4: Analyze the Data
The fourth step is to analyze the data. This involves reviewing the data to determine which causes are most likely to be the root cause of the problem.
Step 5: Identify the Root Cause
The fifth step is to identify the root cause. This involves determining which cause or causes are the underlying cause of the problem.
Step 6: Implement Corrective Actions
The sixth step is to implement corrective actions. This involves developing and implementing solutions to address the root cause of the problem.
Step 7: Monitor the Results
The final step is to monitor the results. This involves tracking the effectiveness of the corrective actions and making adjustments as needed.
Tools and Techniques Used in Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis can be performed using various tools and techniques, including:
- Fishbone diagrams
- 5 Whys
- Fault Tree Analysis
- Pareto Analysis
- Process Mapping
- Statistical Process Control
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Each tool and technique has its advantages and disadvantages, and the selection of the appropriate tool or technique depends on the specific situation and problem being addressed.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in RCA
To ensure the success of the RCA process, it is important to avoid common mistakes, such as:
- Jumping to conclusions without collecting sufficient data
- Focusing only on symptoms and not the root cause
- Blaming individuals instead of focusing on the system or process
- Ignoring possible causes or solutions
- Not involving key stakeholders in the process
By avoiding these mistakes and following the RCA process, organizations can effectively identify the root cause of a problem and develop effective solutions to prevent it from recurring.
Conclusion
Root cause analysis is a crucial process in identifying the underlying causes of problems, events, or incidents. The RCA process helps organizations to understand the root cause of a problem and develop effective solutions to prevent the problem from recurring. By following the seven steps involved in the RCA process, organizations can improve efficiency, reduce risk, and increase customer satisfaction.
FAQs
- Q. What is root cause analysis?
- A. Root cause analysis is a method used to identify the underlying cause of a problem or an event.
- Q. What are the benefits of root cause analysis?
- A. Root cause analysis helps prevent problems from recurring, improves efficiency and effectiveness, reduces risk, promotes a culture of continuous improvement, and increases customer satisfaction.
- Q. What are the steps involved in root cause analysis?
- A. The steps involved in RCA are: Define the problem, Collect data, Identify possible causes, Analyze the data, Identify the root cause, Implement corrective actions, and Monitor the results.
- Q. What tools and techniques can be used in root cause analysis?
- A. Fishbone diagrams, 5 Whys, Fault Tree Analysis, Pareto Analysis, Process Mapping, Statistical Process Control, and Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) are some tools and techniques used in RCA.
- Q. What are some common mistakes to avoid in root cause analysis?
- A. Common mistakes to avoid include jumping to conclusions without collecting sufficient data, focusing only on symptoms and not the root cause, blaming individuals instead of focusing on the system or process, ignoring possible causes or solutions, and not involving key stakeholders in the process.